A Guide to CT Angiography (CTA): Visualizing Blood Vessels
Computed Tomography Angiography, or CTA, is a specialized type of CT scan designed specifically to visualize the body's arteries and veins. It is a powerful, non-invasive test that can provide highly detailed 3D images of the vascular system, allowing physicians to diagnose a wide range of conditions, from blockages and aneurysms to traumatic injuries.
How is a CTA Different from a Regular CT?
While both use the same CT scanner, the key difference is the combination of an intravenous (IV) iodine-based contrast injection and precise scan timing.
- IV Contrast Injection: A power injector is used to rapidly administer the contrast agent into a vein, usually in the arm. This makes the blood appear bright white on the scan.
- Scan Timing: This is the most critical element. The technologist must time the start of the scan perfectly to coincide with the moment the contrast-filled blood reaches the specific arteries or veins of interest. This "bolus tracking" is often done using a monitoring scan that detects when the contrast arrives at a target location.
By scanning at this peak moment of vessel enhancement, the CTA can capture a clear and detailed map of the vascular anatomy.
Post-Processing: Creating the 3D Images
After the raw, thin-slice images are acquired, a technologist or radiologist uses specialized software to post-process the data. This involves digitally removing structures that are not needed (like bones and organs) to isolate the blood vessels. The software can then create stunning 3D reconstructions that can be rotated and viewed from any angle.
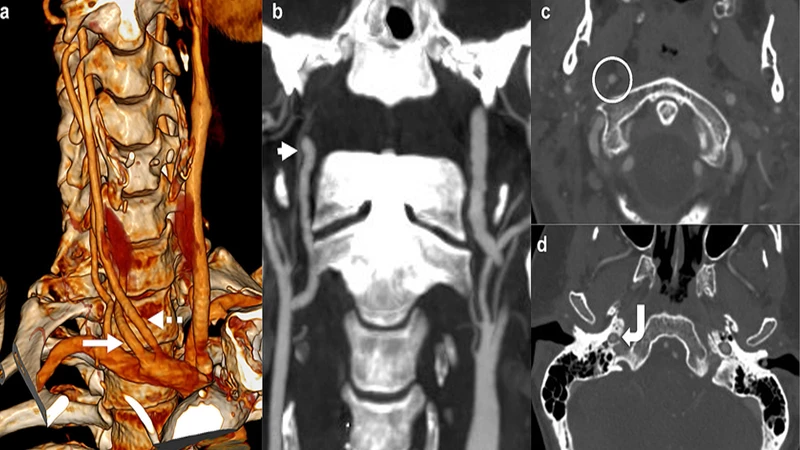
Common Applications of CTA
CTA is used to examine blood vessels throughout the body. Some of the most common exams include:
- CTA of the Head & Neck: Used to detect aneurysms, blockages (stenosis) in the carotid arteries that can lead to stroke, and vascular malformations.
- CTA of the Chest (Pulmonary Embolism Study): A life-saving emergency exam to find blood clots in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs.
- Coronary CTA: A non-invasive way to visualize the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart, used to detect plaque and blockages.
- CTA of the Abdomen & Pelvis: To evaluate the aorta for aneurysms or dissection, and to assess the blood supply to organs like the kidneys and liver.
- CTA of the Runoffs: To examine the arteries in the legs to diagnose peripheral artery disease.
Conclusion: A Clear Map of the Vascular System
CT Angiography has become an indispensable tool in modern radiology. Its speed, accuracy, and ability to generate detailed 3D images provide physicians with a clear and comprehensive road map of a patient's vascular system. This allows for rapid diagnosis of potentially life-threatening conditions and plays a crucial role in planning for both surgical and minimally invasive interventional procedures.

Comments